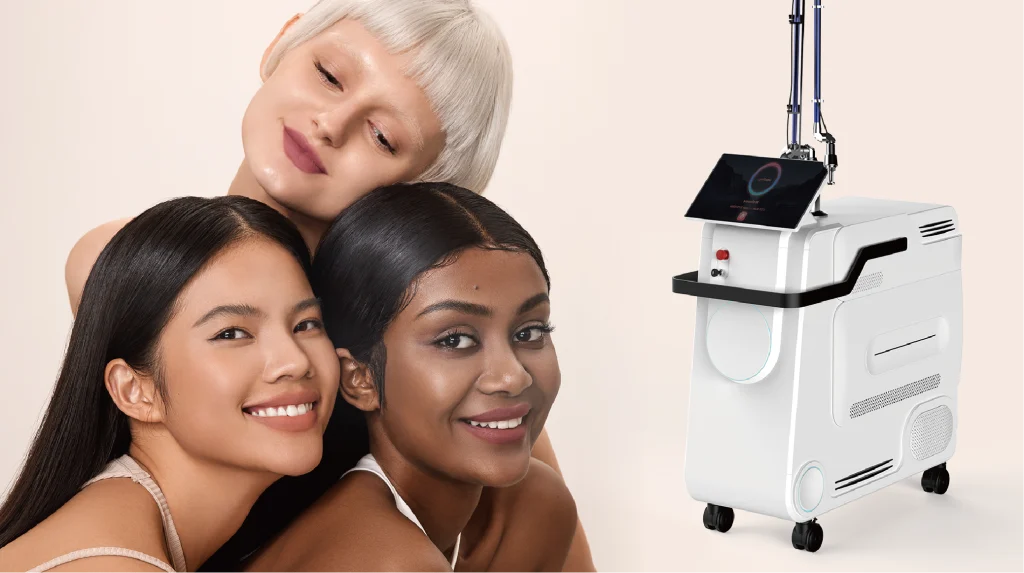
1927 nm Thulium Fractional Laser: Safe & Effective for PIH and Acne
Introduction
Fractional laser technology has transformed modern dermatology and aesthetic medicine. With the growing demand for safe and effective treatments that address both pigmentation and textural skin concerns, particularly in patients with darker skin types, the 1927 nm thulium fractional laser has emerged as a leading modality. Compared to traditional wavelengths such as 1550 nm and 10,600 nm CO₂ lasers, the 1927 nm wavelength provides unique clinical advantages, including improved water absorption, shorter downtime, and enhanced efficacy in pigmentation disorders. This article explores the mechanism, clinical applications, advantages, and comparative benefits of the 1927 nm thulium fractional laser.
Mechanism of Action
The 1927 nm wavelength is characterized by strong water absorption, making it highly effective in targeting the epidermis and superficial dermis. Compared to the 1550 nm laser, the 1927 nm demonstrates superior water affinity, leading to more controlled epidermal resurfacing. While the 10,600 nm CO₂ laser is the strongest in terms of water absorption and ablative effect, its downtime is considerably longer.
Through selective photothermolysis, the 1927 nm laser promotes controlled microthermal injury zones, stimulating skin regeneration while maintaining safety. Its epidermal focus makes it particularly well-suited for pigmentation disorders and superficial resurfacing, while still offering follicular remodeling for acne treatment.
Clinical Applications
Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH)
A pilot study has shown that low-energy, low-density, non-ablative fractional 1927 nm wavelength laser treatment, followed by topical hydroquinone 4% cream for six weeks, is a safe and effective modality for improving PIH in patients with darker skin types. The risk of rebound hyperpigmentation is minimized, making this wavelength especially suitable for Fitzpatrick skin types IV–VI.
Active Acne and Acne Scars
The 1927 nm thulium laser demonstrates significant potential in treating active acne. Its water absorption characteristics allow targeted heating of the follicular infundibulum and sebaceous glands, thereby reducing Cutibacterium acnes proliferation and oil gland activity. Recent studies highlight its role in follicular remodeling, making it an attractive option for acne management. While fractional CO₂ lasers remain highly effective for atrophic acne scar remodeling, their prolonged erythema and downtime limit their use. In contrast, the 1927 nm laser offers a balance of efficacy and patient tolerability.
Skin Rejuvenation and Texture Improvement
Beyond pigmentation and acne, the 1927 nm thulium laser has proven effective in improving overall skin quality. Patients report significant improvements in fine lines, enlarged pores, and uneven skin tone. Its superficial penetration ensures safer outcomes, even in skin of color.
Advantages of the 1927 nm Thulium Laser
- Minimal downtime: Shorter erythema and recovery compared to ablative CO₂ lasers.
- Safe for darker skin: Reduced risk of post-treatment hyperpigmentation.
- Effective dual action: Addresses both pigmentation and textural irregularities.
- Customizable settings: Low-energy, low-density protocols enhance safety while delivering results.
Comparison with Other Wavelengths
- 1550 nm fractional laser: Offers deeper dermal penetration and collagen remodeling, making it highly effective for acne scars and skin laxity. However, its water absorption is lower compared to 1927 nm, making it less ideal for pigmentary concerns.
- 10,600 nm CO₂ fractional laser: Remains the gold standard for severe atrophic acne scar remodeling due to its ablative power. However, longer downtime and higher risk of PIH limit its use in darker skin types.
- 1927 nm thulium fractional laser: Provides the best balance of safety and efficacy for epidermal pigmentation disorders, active acne, and superficial skin rejuvenation, with a shorter recovery period.
Safety and Patient Experience
The 1927 nm laser has shown excellent safety in clinical practice. By using low-density settings, practitioners can minimize adverse effects such as erythema, edema, or PIH. When combined with post-procedure care including topical hydroquinone and sun protection, patients experience significant improvement with minimal complications. Clinical studies confirm high satisfaction rates and sustained results.
Conclusion
The 1927 nm thulium fractional laser represents a breakthrough in aesthetic dermatology. Its superior water absorption, shorter downtime compared to CO₂ lasers, and safety in darker skin types make it an invaluable tool for treating PIH, active acne, and superficial rejuvenation. As evidence continues to grow, the 1927 nm wavelength is increasingly regarded as a gold-standard solution for pigmentation disorders and early textural changes, offering both efficacy and safety.
For aesthetic practices and dermatology clinics seeking a versatile, patient-friendly technology, the 1927 nm thulium laser stands out as a must-have device.