Laser Pigmentation Removal: How It Works and What Results to Expect
Hyperpigmentation – dark spots, sun damage, post-acne marks or melasma – is one of the most common cosmetic concerns worldwide. Professional societies such as the American Academy of Dermatology point out that some dark spots can fade on their own over 6–12 months, but deeper pigment may persist for years and often needs medical treatment.
Among in-clinic options, laser pigmentation removal has become a key procedure because it can target excess melanin very precisely while leaving surrounding skin relatively unharmed. Dermatology sources also list laser and intense pulsed light (IPL) among first-line procedures for age spots and photo-damage when performed by trained professionals.
If you’d like to explore the most common patient questions about this treatment, you can visit our full FAQ guide here. Laser Pigmentation Removal FAQs
What is Laser Pigmentation Removal?
Laser pigmentation removal is a non-surgical treatment that uses concentrated beams of light to break up unwanted pigment in the skin. Clinics commonly use it for:
- Sun spots and solar lentigines
- Freckles and photo-damage
- Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) after acne or procedures
- Some café-au-lait macules, birthmarks and other benign pigmented lesions
Authoritative dermatology reviews emphasize that while laser and light devices can improve many pigmentary disorders, conditions like melasma and darker skin phototypes require special caution because of the risk of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation and recurrence. For these patients, device choice, wavelength, pulse duration and settings are critical, and treatment is usually combined with topical skincare and strict sun protection rather than relying on laser alone.

How Does Laser Pigmentation Removal Work?
1. Targeting melanin with selective photothermolysis
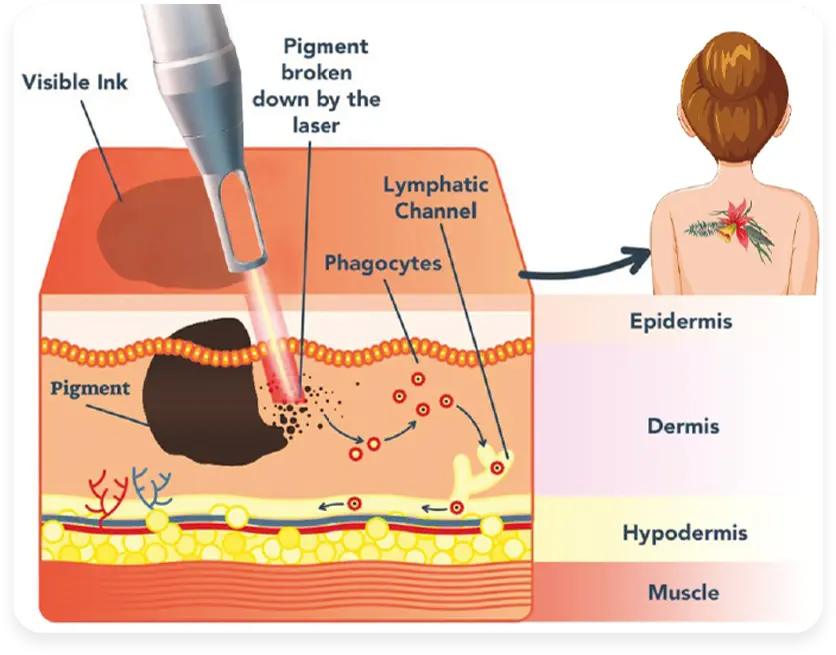
Most pigmentation lasers are based on selective photothermolysis – a principle where a specific wavelength of light is absorbed by a particular target (chromophore) more than surrounding tissue. In pigmentation treatment, the target is melanin inside melanocytes or melanosomes.
When laser light of an appropriate wavelength hits the skin, pigmented cells absorb more of that energy than normal tissue. This causes very localized heating or stress within the melanosomes, damaging them while sparing most of the surrounding structures. Over the following days to weeks, the fragmented pigment is gradually cleared through the skin’s natural turnover and immune system. Clinical resources and clinic case series consistently describe this sequence: laser energy → melanin absorption → pigment fragmentation → gradual elimination.
The degree of melanin absorption depends strongly on wavelength. Shorter wavelengths (for example 532 nm) are absorbed more strongly by melanin but penetrate less deeply; longer wavelengths (such as 755 or 1064 nm) penetrate deeper with relatively less melanin absorption, which can be safer for darker skin types when used correctly.
2. Nanosecond vs. picosecond: photothermal vs. photoacoustic effects
Traditional pigment lasers like Q-switched Nd:YAG or ruby lasers deliver energy in nanosecond pulses. These devices mainly work through a photothermal effect: melanin absorbs laser energy, heats up and is destroyed by rapid temperature rise.
Modern picosecond lasers deliver much shorter pulses – on the order of 10⁻¹² seconds. Clinical and technical comparisons show that picosecond systems create a stronger photoacoustic (mechanical) effect with less reliance on heat, shattering melanin into finer particles that the body can clear more efficiently while reducing collateral thermal damage. This shift from primarily heat-based injury to mechanical disruption is one reason picosecond lasers are increasingly favored for both tattoos and benign pigmentation.
3. Fractional delivery and skin remodeling
Many newer platforms also offer fractional handpieces. Instead of delivering energy in a solid spot, the beam is split into an array of micro-beams that create microscopic zones of injury surrounded by intact skin. Studies on fractional picosecond lasers report improvements in facial dyspigmentation, pores, wrinkles and atrophic scars, along with pigment clearance.
Some fractional picosecond tips are designed to induce laser-induced optical breakdown (LIOB) within the dermis – tiny cavitation bubbles or “microwounds” that stimulate collagen remodeling while leaving the epidermis largely intact. This approach can combine pigment improvement with overall texture and rejuvenation in a single session.
What Results Can Patients Expect?
1. Which pigment problems respond best?
Evidence from dermatology organizations and clinical practice suggests that laser pigmentation removal is particularly effective for:
- Solar lentigines / age spots – often improved significantly in one or a few sessions.
- Freckles and sun damage – diffuse mottled pigmentation typically requires several sessions but can show visible brightening and a more even tone.
- Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) – selected cases may benefit once the underlying inflammation is controlled, though over-treatment can sometimes worsen discoloration.
Melasma is more complex. Reviews highlight that while lasers (including fractional and Q-switched devices) can produce short-term improvement, relapse and PIH are common, especially in skin of colour. For melasma patients, many dermatologists recommend conservative settings, longer intervals between sessions, and combining laser with topical brighteners and strict UV protection rather than aggressive, high-energy treatment.
2. How many sessions are typically needed?
The number of sessions depends on the type and depth of pigmentation, skin type, and device used. Clinical guidance and patient information from organizations like the AAD and Mayo Clinic note that:
- Discrete age spots may respond in 1–3 sessions.
- Diffuse sun damage or freckles usually need a series of treatments spaced several weeks apart.
- Complex conditions such as melasma require multiple conservative sessions, and results may be partial or temporary.
Patients should be counselled that pigment will often look darker or more “peppered” right after treatment before flaking or fading over 1–3 weeks, and that full results are assessed over several months.
3. Side effects, downtime and safety
Short-term effects commonly include redness, mild swelling and a sensation similar to sunburn, typically resolving within hours to a few days, depending on fluence and whether fractional modes are used. More intensive resurfacing lasers, such as ablative CO₂, can require 1–2 weeks of recovery.
Potential complications highlighted in dermatology literature include:
- Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) or hypopigmentation, particularly after aggressive treatments or in darker skin types.
- Temporary crusting or blistering
- Very rarely, scarring or textural change when parameters or aftercare are inadequate
Because of these risks, guidelines emphasise choosing a provider experienced with different lasers and with treating a wide range of skin tones, especially Fitzpatrick IV–VI.
4. The importance of sun protection and skincare
Professional associations consistently stress that sun protection is non-negotiable. Ongoing UV exposure is a major driver of hyperpigmentation and recurrence, and patients are advised to use broad-spectrum sunscreen, protective clothing and behavioural measures every day.
Brightening skincare – such as formulations containing vitamin C, azelaic acid, retinoids or other pigment modulators – is often recommended alongside procedures to maintain results and reduce relapse risk, especially in melasma.
Why Picosecond Platforms Are Changing Laser Pigmentation Removal
Over the last decade, picosecond laser systems have reshaped expectations for Laser Pigmentation Removal. Comparative articles and clinic data highlight several advantages over older nanosecond Q-switched devices:
- Shorter pulse duration (picoseconds vs nanoseconds) delivers energy so rapidly that a strong photoacoustic shockwave is generated, shattering melanin into very fine particles.
- Less thermal diffusion into surrounding tissue can translate into reduced downtime and a lower risk of PIH, particularly important for darker skin phototypes when parameters are chosen conservatively.
- Fractional picosecond tips allow simultaneous treatment of pigment, texture and pores through dermal remodeling while keeping the epidermis largely intact.
For clinics, this means an opportunity to offer pigment, tattoo and rejuvenation services with one platform, while giving patients faster visible results and shorter recovery in many cases.

Ultra PicoMax: A Versatile Picosecond Platform for Pigmentation Clinics
For clinics and distributors looking to build a strong Laser Pigmentation Removal portfolio, a device like Ultra PicoMax is designed to combine clinical versatility with practical workflow features. According to the manufacturer’s technical information, Ultra PicoMax offers:
- Three core wavelengths in one standard applicator – 1064 nm, 532 nm and 755 nm – plus optional 585 nm and 650 nm tips, covering a wide range of pigmented lesions, tattoos and skin types.
- 350 ps pulse width delivering true picosecond energy for efficient photoacoustic breakdown of melanin and tattoo ink.
- Multiple operating modes including Picosecond, PTP, Multi-Pulse and Long Pulse, allowing parameter optimisation for epidermal spots, deeper chloasma, stubborn stains and even vascular or rejuvenation indications.
- A Honeycomb HP fractional handpiece that scatters the beam into tiny spots to induce laser-induced optical breakdown (LIOB) in the dermis, promoting collagen remodeling while leaving the epidermis intact – useful when combining pigment improvement with overall skin rejuvenation.
- A customised seven-joint arm with ≤8% energy loss and 360° rotation, designed to keep fluence consistent across treatment areas and make long sessions less fatiguing for the operator.
- Regulatory credentials including CE marking and FDA clearance for specific indications, along with clinical publications supporting its use in pigmented lesions, tattoo removal and rejuvenation.
For patients, this type of platform can translate into:
- More tailored treatments for different pigment types and skin tones
- The possibility of combining pigment clearance with texture and pore improvement
- Minimal downtime in many protocols, with only transient redness reported in most routine sessions
Of course, every clinic still needs to adapt parameters to local regulations and individual patient profiles, and laser procedures should always be performed by trained professionals with informed consent.
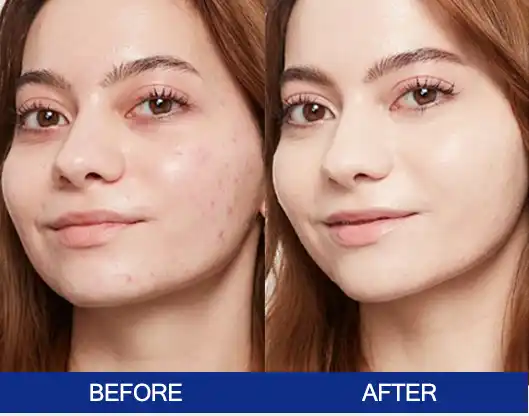


Final Thoughts
Laser Pigmentation Removal is not a magic eraser, but when it is grounded in sound physics, careful diagnosis and realistic expectations, it can deliver very meaningful improvements in dark spots, sun damage and certain pigmentary conditions. Modern picosecond systems with multiple wavelengths and fractional options give clinics more control over how energy is delivered into melanin and the dermis, helping to balance efficacy with safety – especially in patients at higher risk of PIH.
For clinics and partners who want to build a sustainable pigmentation program, focusing on three pillars tends to work best:
- Careful patient selection and diagnosis (including when not to use aggressive lasers, such as unstable melasma).
- Evidence-based Laser Pigmentation Removal protocols combined with sun protection and topical skincare.
- Reliable, versatile technology such as a multi-wavelength picosecond platform, supported by solid training and after-sales service.
If you want to obtain more information, please follow our official website and Facebook.









